Coauthored by Dominick Bitting, Sr. Threat Research Analyst, and Colin Maguire, Web Content Specialist.
Manchester City win the Carabao Cup Final, many illegal streamers lose
The COVID pandemic has led to a surge in content consumption as people stayed home and turned to Netflix, Youtube and other streaming services for entertainment. Not everyone agrees with paying for the latest episode or album, however, and this rise has ran parallel with a rise in digital piracy.
Piracy is widespread and – ethical issues aside – makes for an interesting case study from a threat research perspective. In terms of sports, European football is the most commonly pirated, making up more than a quarter of all illegal sports streams according to one recent study.
There is a sizable online community that shares bootlegged movies, TV and live sports streams without copyright protection over HTTP/HTTPS. Sites streaming pirated sports, specifically the English football “free-to-view” sites, were the subject of an April 2021 Webroot study on the week of the Carabao Cup final game between Manchester City and Tottenham Hotspur.
This was not meant to be an exhaustive study, but rather focused on getting a snapshot of the dangers involved in spending 90 minutes illegally streaming a match online.
The sites we analysed
We analysed a total of 20 sites in the study, of which 12 “game sites” were analysed in greater detail for the duration of the Cup Final. 92% per cent of illegal streaming sites analysed by Webroot were found to contain some form of malicious content.
Site Ratings
Sites ranged from having a “trusted” Webroot Brightcloud® reputation score of 92 to an “untrusted” rating of 44. All sites at time of testing had a safe, zero detection rating in Virus Total except for one, “daddylive”, with a rating of 1/85.
However, when examined more closely, most hosting IPs were found to have hosted malicious content (such as some serious malware) in the past, and had connections to other high-risk IPs. Some of the sites caught our attention for leading to a massive amount of URLs. For instance, rojadirecta[.]me pulled 565 different URLs. We focused most of our attention on these suspicious sites.
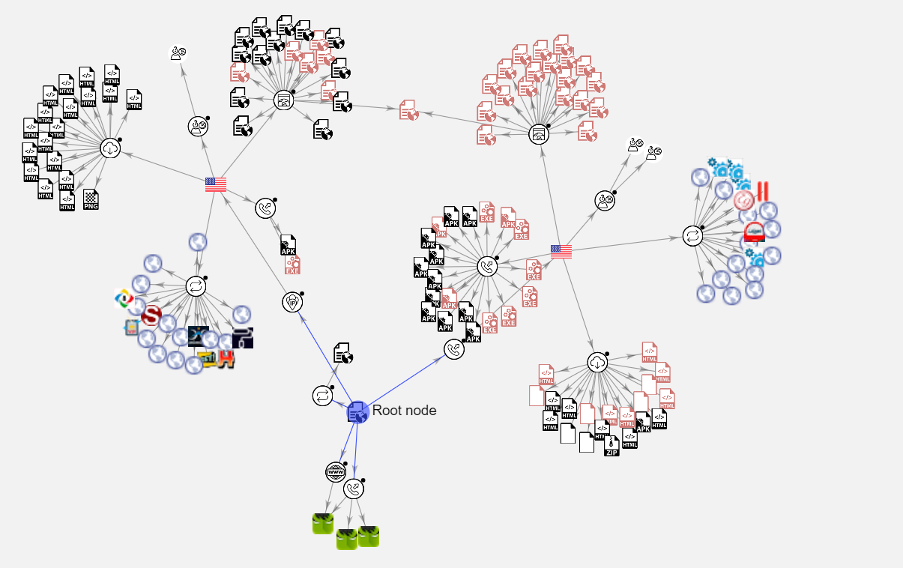
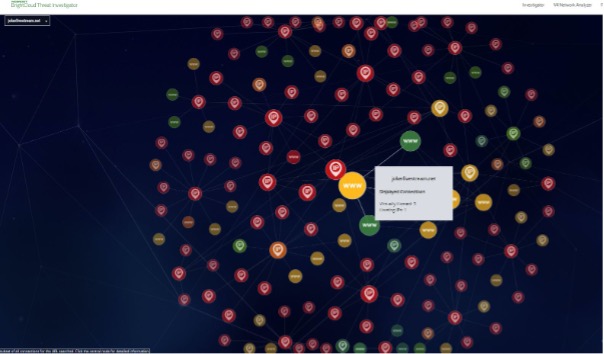
Insecure Sites
Most of the sites analysed were insecure and running HTTP. The lack of security on these sites means any personal data shared across the site’s connection is out in the open. While the more secure HTTPS isn’t always a guarantee a site is completely safe, the lack of certification and security protocol were red flags, making sharing details or sensitive information risky.
Malvertising/Dishonest links
Most of these sites (more specifically the advertising on these sites) use dishonesty and social engineering to fool users into opening links, enabling an action on their browser or downloading a file they never intended to. This is done using an array of tricks like fake “X” boxes on video overlays, false “notification enable” messages and outrageous promises and warnings.
Redirects
Redirects are not bad in and of themselves, but when links jump between a number of unrelated sites (e.g. sports to dating to bitcoin to online shopping) this is a definite red flag. And we observed it a lot on illegal streaming sites. This signals that the site or site network admins must constantly change what their links direct to as they introduce new URLs. The presence of zero-day (or brand new) sites is a related bad indicator when looking at any site and it’s connected IPs.
Types of threats we saw on pirated streaming sites
Bitcoin scams
“With cryptocurrency values soaring again, executable based cryptojacking has been on the rise.”
Webroot’s 2021 Threat Report
We observed targeted and localised bitcoin scams promising riches and asking users for banking details. The price of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have been booming over the last year, and the rise and fall of these prices affects cryptocrime levels. We observed convincing ads and websites that link directly to fake news sites or feature local(ised) celebrities and politicians selling scams.
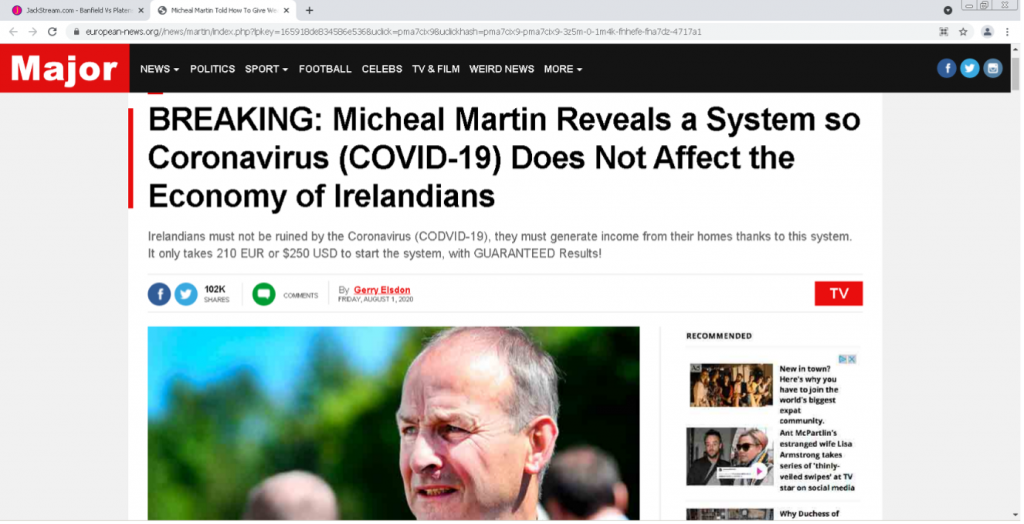
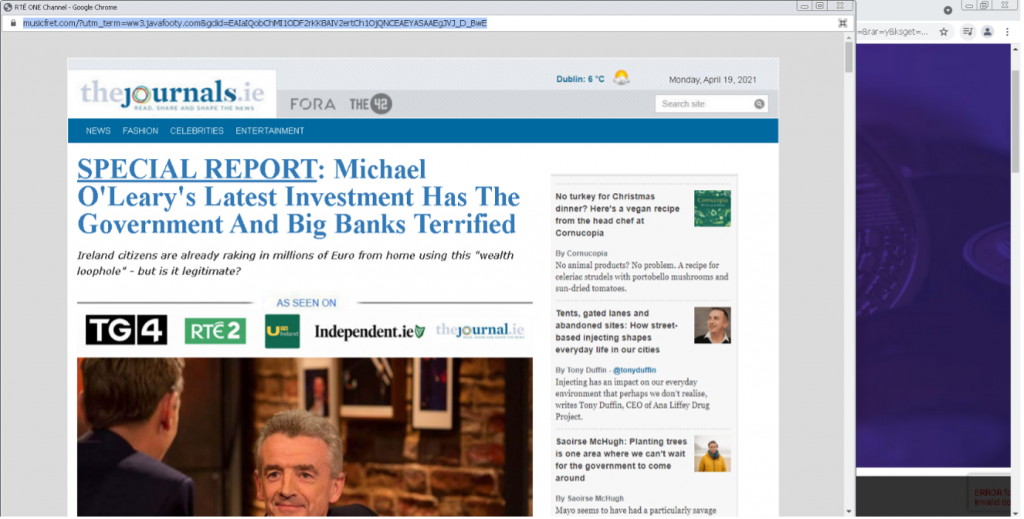
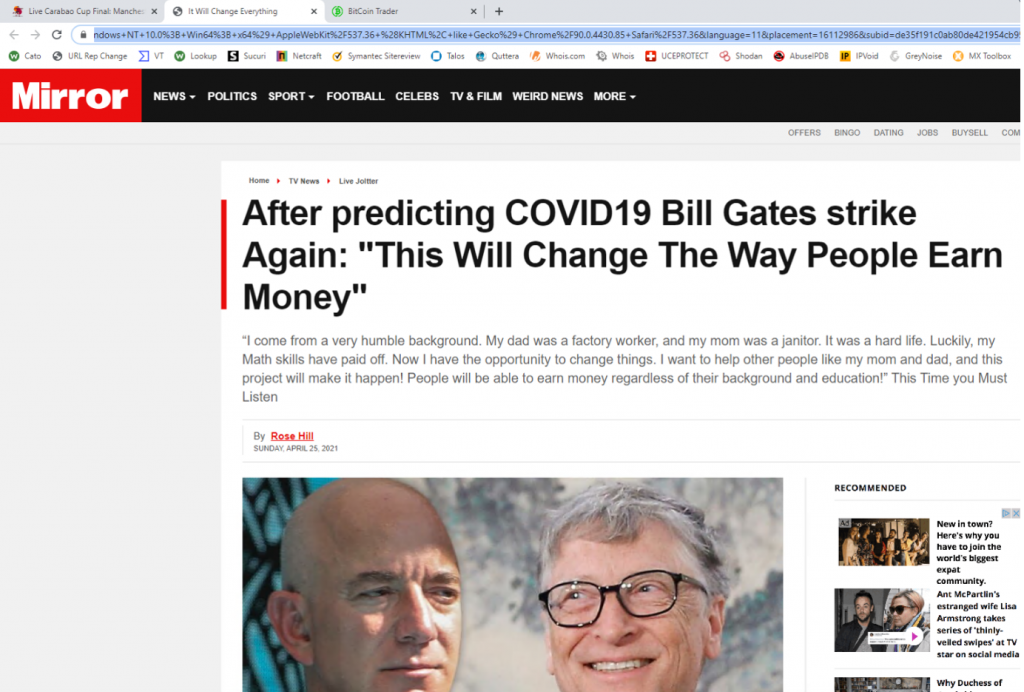
This “Mirror” fake news page is clearly designed to copy the popular UK newspaper. It is a front for a “get rich quick” scam designed to gather users’ cash and personal details. Different versions of this scam have been observed localised for different countries. This was pushed on the vipleague[.]lc streaming site.
“Appearing on the ‘BBC Breakfast’ show, Bill Gates revealed that he invested substantial amounts of money. The idea was simple: allow the average person the opportunity to cash in…”
Text from one scam we witnessed
Hijacked search results
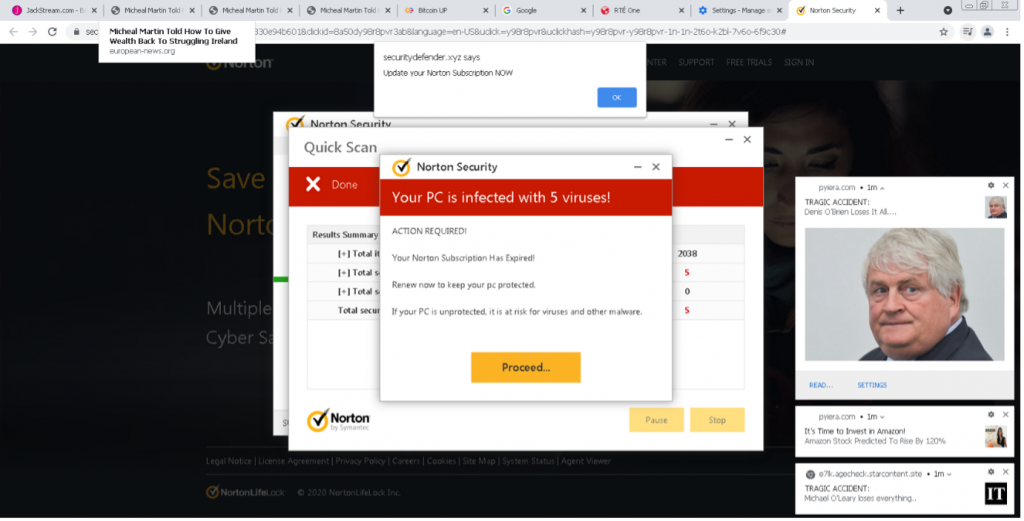
Hijacking browsers allows cybercriminals to switch a user’s default browser and take over its notifications. This means different search results are served up or users can be spammed with junk notifications and explicit content. Even if users shut down their laptops, the changes will remain.
Notification hijacking
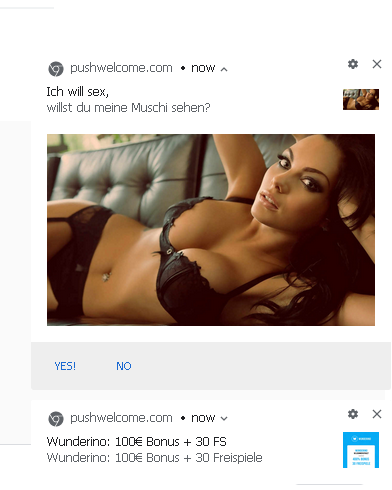
Users looking to watch a stream are also tricked into allowing notifications, which bombard them with explicit and extreme content, as well as scams and links to other malicious sites.
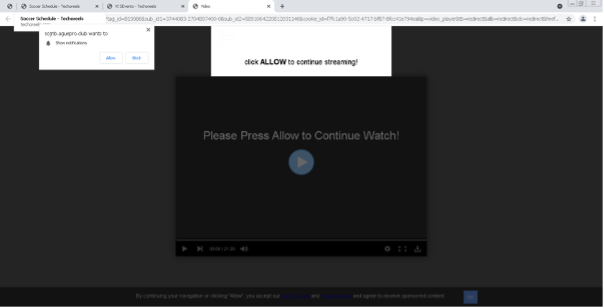
Browser Hijacker
Links on jackstream. push users into installing a browser hijacker known as mysearchflow.com, which is blocked as Spyware/Adware by Webroot. Clicking on the stream causes a popup which asks to allow notifications. These particular notifications were pop-up ads appearing in the screen’s right corner that were very intrusive and not easy to disable.
Mobile Threats
All these sites supported mobile browsing and the advertising, social engineering and malicious content targeting mobile users, too. For instance, links pointed to fake mobile apps with privacy issues and useless in-app purchases ranging from £2.09 – £114.99. It’s important for users to note that many of these mobile apps can also be installed on PCs and are often difficult to remove. Here’s a mobile advertisement from hulkstreams.com that earns clicks by claiming a device is infected with viruses.
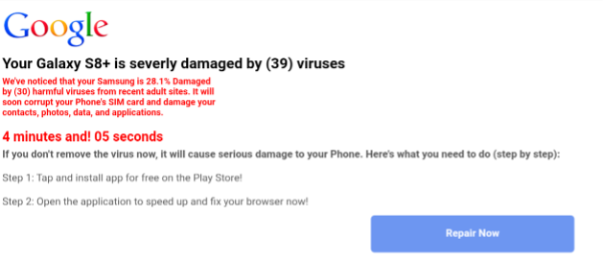
We installed and ran this particular product. It turned out to be an example of fleeceware, a type of malware that tries to sneak excessive fees past subscribers. It had over 10 thousand downloads on the Google Play store already. The product offered in-app purchases ranging from £2.09 – £114.99 per item and has since been marked as malicious by our threat intelligence.
| The sites we analysed. Starred sites indicate “game sites.” |
| hulkstreams.com* |
| jackstreams.com* |
| 0eb.net* |
| jokerswidget.com* |
| strims.world* |
| livetotal.tv* |
| vipleague.lc* |
| fotyval.com* |
| footybite.com* |
| daddylive.co/* |
| elixx.me/schedule.html*hdstreamss.club/* |
| liveonscore.tv/ |
| red.soccerstreams.net/ |
| www.blacktiesports.net/soccerstreams/ |
| www.hesgoal.com/ |
| www.ovostreams.com/soccer-streams.php |
| www.sportnews.to/schedule/ |
| www.sportp2p.com |
Our advice
Since pirate streams operate outside the law, they often sell advertising space to entities that are also operating outside the law. Although we found some advertising from reputable vendors, we would not recommend visiting these sites for the good of your overall online safety.
We do recommend that, when browsing any site on the web, users update their software and operating systems, employ AV and anti-phishing detection, and double-check any links before clicking, especially when they profess to offer something that seems too good to be true.






