Would You Like To Know My Social Security Number?
It’ll cost you a buck. Just like everyone else’s. The use of a Social Security Number (SSN) as unique identifiers has long been a contentious subject. SSNs were never intended to be used for identification, and their ubiquitous abuse for identification and authentication has lead me to call them “Social Insecurity Numbers,” or SINs.
There was a time when my response to a breach that leaked SSNs was “the horror, the horror.” Now my cynical reaction is “big deal, they stole my public information… again.” Yes, I know it’s improper for a security expert to feel this way, but an improper response is sometimes still the correct response.
Let me walk you through both sides of the issue: the horror and the dispassion.
The Horror
When aliens visit our lifeless planet in 2525, they will run DNA tests on our remains and they will catalog or index us by our SINs. That’s one of the things that makes the theft of SSNs worrisome. SSNs do not expire. A person may expire, their SSN does not. Social security numbers are not reused. They just stop being used. Funds may be paid to surviving spouses and children, but after that the SSNs are a permanent entry in a database.
Let’s put this into perspective. Of all of the credit cards issued between 1946 and 2012, virtually none are valid. Of all of the compromised credit cards issued between 2012 and 2018, very few remain valid. Sometimes the cards are replaced before they’re fraudulently used, and other times fraudulent use results in the cancellation of the cards. In either case, the cards are simply replaced with new account numbers.
Compare this to SSNs. Of all of the SSNs issued since 1934, well… Have you ever see an expiration date on a Social Security card? You can change your credit card number. You can change bank. You can change your career, your doctor, your vet, your clothes, or your mind. But unless you enter the United States Federal Witness Protection Program, your SSN isn’t changing. (Actually, that’s a bit overstated. Under certain circumstances you can get a new SSN, but your SSN simply being compromised does not qualify you to change SSNs.)
According to a study published by Javelin, more social security numbers were involved in breaches in 2017 than credit cards. Think about that for a moment. Do you know anyone who has had a fraudulent purchase made on their credit card? Here’s where the problem becomes insidious. Credit card fraud is loud. You can hear it coming. I have alerts set up on my bank accounts so that I know each time a charge is made. I am alerted through text and email. One fraudulent charge and I know. I can act.
But SSNs are quiet. Multiple applications for credit cards can be made simultaneously, but you’re not likely to find out very quickly. Pair this with a compromised email account, and you could be in big trouble. For me, it’s of serious concern.
The Dispassion
Why don’t I worry about my SSN being leaked? Because it’s already been leaked multiple times in multiple breaches.
How do I know that?
I don’t, I just assume it has been. Why? Because my SSN has been vulnerable to theft for decades, and there are so many compromised SSNs stocking the dark web that they’re a cheap commodity. You might even expect to encounter a “buy five credit card numbers get two SSNs free” deal, or to see them sold by the dozen, like Kleenex at Costo.
According to Brian Stack, the Vice President of Dark Web Intelligence at Experian, Social Security numbers sell for only $1 on the dark web. In the massive Marriot breach, it wasn’t my SSN I was worried about, it was my loyalty program information. My loyalty program information is worth 20 times more than my SSN on the dark web. Loyalty program points can be used to buy travel or merchandise in airline shopping malls.
For several years, “assume the breach” has been the mindset of many security professionals, meaning that we should assume a company will be breached, or already has been breached, and we should be clear-eyed about it. It is a call to action. Put mitigations and remediation processes in place. Have an action plan.
For the public, and I cannot emphasize this enough, this means you should assume it was your data that was compromised in the breach, and put a remediation plan in place. If the businesses holding your data assumes your data is toast, then you should too.
What You Can Do
So, if we’re adopting the fatalist position on SSN theft, but still want to protect ourselves, what’s a person to do?
- Credit freezes and fraud alerts. Both are good proactive defenses. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is a good place to start if you don’t know how. For information about credit freezes, check here. For information about fraud alerts and extended fraud alerts, take a look here and here.
- Use two-factor authentication. Gmail, Facebook, Twitter, and other sites offer two-factor authentication. Typically, this means you’ll need to respond to a text or email in order to log into your account. This makes it harder for the bad guys to hijack it. Not impossible, but significantly more difficult.
- Take advantage of alerts offered by financial institutions. If someone tries to log into my bank account or make a charge on my credit or debit card, I will know it immediately.
- Be Prepared for Identity Theft. Once again, the FTC consumer information page on identity theft is a great resource for consumers, security evangelists, and businesses alike on how to build a strong defensive posture.
Identity theft is real, it can be devastating, and you need to be prepared for it. But reports of breaches that include SSNs tell me what I already know; my SSN is in the hands of cybercriminals. It has been for years.
So no, I’m not going to tell you my SSN. You’ll have to pay your dollar for it, just like everyone else.
A Miner Decline: The Slowdown of a Once-Surging Threat
This is the first of a three-part report on the state of three malware categories: miners, ransomware and information stealers.
In Webroot’s 2018 mid-term threat report, we outlined how cryptomining, and particularly cryptojacking, had become popular criminal tactics over the first six months of last year. This relatively novel method of cybercrime gained favour for being less resource-intensive and overtly criminal when compared to tactics involving ransomware. But mining cases and instances of mining malware seem to have dropped off significantly in the six months since this report, both anecdotally and in terms of calls to our support queue.
The crytpo world has gone through significant turmoil in this time, so it’s possible the reduced use of malicious cryptojacking scripts is the result of tanking cryptocurrency values. It’s also possible users are benefitting from heightened awareness of the threat and taking measures to prevent their use, such as browser extensions purpose-built to stop these scripts from running.
Setting aside the question of why for a moment, let’s take a look at some stats illustrating that decline during that time period.
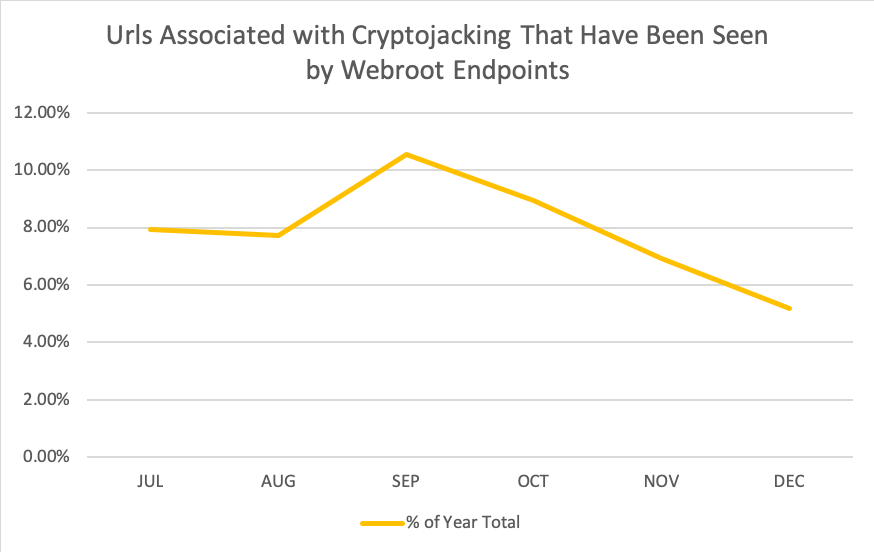
Cryptojacking URLs seen by Webroot over six months beginning 1 July through 31 December, 2018, Webroot SecureAnywhere client data.
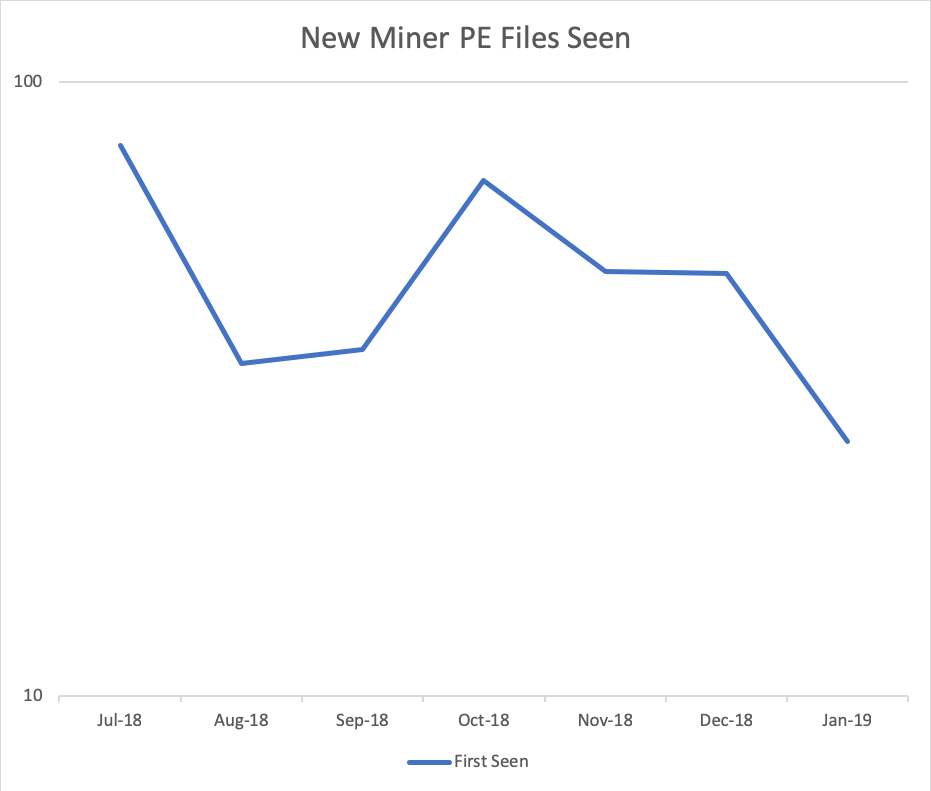
New miner malware seen by Webroot
Data from six months beginning 12 July through 9 Jan, 2019, Webroot data, units logarithmic.
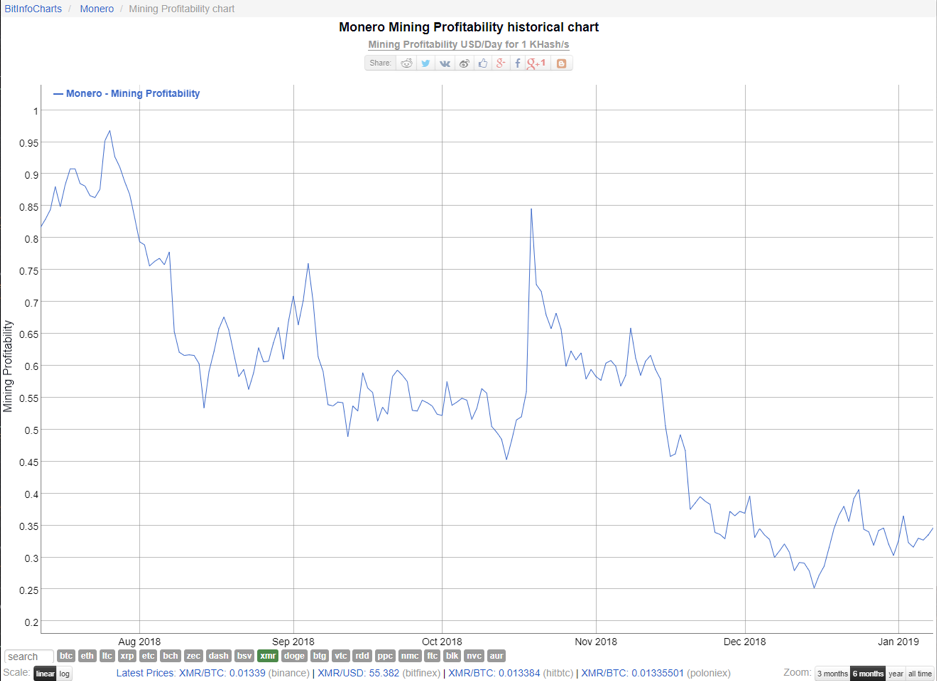
Monero mining profitability ($)
Data covering six months from 12 July – 9 Jan, 2019, Bit Info Charts, units logarithmic
Monero price ($)
Data covering six months from 12 July through 9 Jan, 2019, World Coin Index
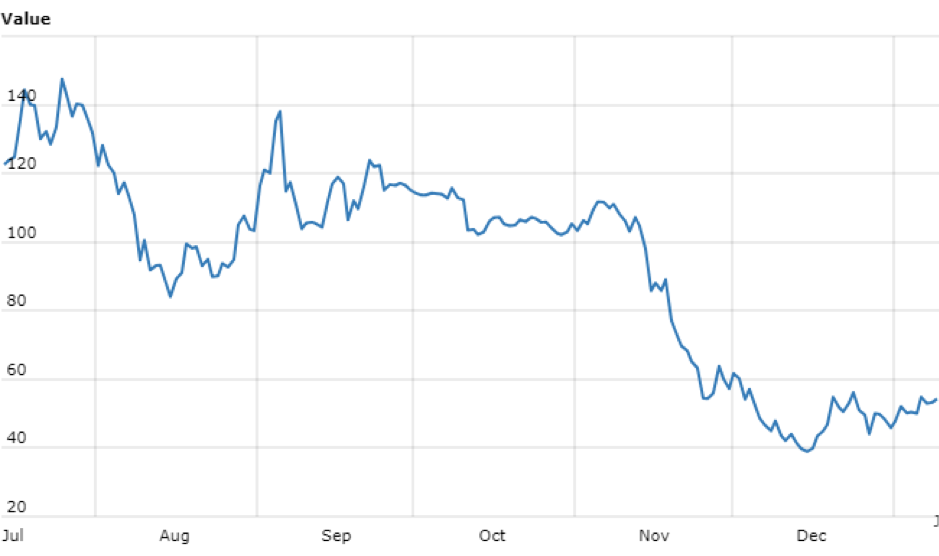
Interpreting the data
None of the graphs are identical, but without too much statistical comparison, I think a broad trend can be seen: malicious mining is on the decline alongside a general decline in coin value and coin mining profitability.
Profitability affecting criminal tactics is of course not surprising. The flexibility of exploit kits and modern malware campaigns like Emotet mean that cybercriminals can change tactics and payloads quickly when they feel their malware isn’t netting as much as it should.
Thanks to the dark web, criminal code has never been easier to buy or rent than in recent years, and cryptocurrencies themselves make it easy to swap infection tactics while keeping the cash flowing. Buying or renting malicious code and malware delivery services online is easy, so the next time the threat landscape changes, expect criminals to quickly change with it.
Should I still care about miners?
Yes, absolutely.
Cryptocurrency, cryptomining, and malicious cryptomining aren’t disappearing. Even with this dip, 2018 was definitely a year of overall cryptocrime growth. Our advanced malware removals teams often spot miner malware on machines infected by other malware, and it can be an indication of security holes in need of patching. And any illegal mining is still capable of constantly driving up power bills and frustrating users.
Where are cybercriminals focused now?
Information theftis the current criminal undertaking of choice, a scary development with potentially long-lasting consequences for its victims that are sometimes unpredictable even to thieves. The theft, trade, and use for extortion of personal data will be the focus of our next report.
What can I do?
Cryptojacking may only be on the decline because defences against them have improved. To up your chances of turning aside this particular threat, consider doing the following:
- Update everything. Even routers can be affected by cryptojacking, so patch/update everything you can.
- Is your browser using up lots of processor? Even after a reset/reinstall? This could be a sign of cryptojacking.
- Are you seeing weird spikes in your processor? You may want to scan for miner infections.
- Don’t ignore repeated miner detections. Get onto your antivirus’ support team for assistance. This could be only the tip of the iceberg.
- Secure your RDP.
What can Webroot do?
Webroot SecureAnywhere®antivirus products detect and remove miner infections, and the web threat shield blocks malicious cryptojacking sites from springing their code on home office users. For businesses, however, the single best way to stop cryptojacking, is with DNS-level protection. DNS is particularly good at blocking cryptojacking services, no matter how many sites they try to hide behind.
Persistent mining detections might point to other security issues, such as out-of-date software or advanced persistence methods, that will need extra work to fix. Webroot’s support is quick and easy to reach.
In the end, cryptomining and cryptojacking aren’t making the same stir in the cybersecurity community they were some months ago. But they’ve far from disappeared. More users than ever are aware of the threat they pose, and developers are reacting. Fluctuations in cryptocurrency value have perhaps aided the decline, but as long as these currencies have any value cryprojackers will be worth the limited effort they require from criminals.
Watch for the use of cryptominers to be closely related to the value of various cryptocurrencies and remain on the lookout for suspicious or inexplicable CPU usage, as these may be signs that you’re being targeted by these threats.
And of course, stay tuned to the Webroot blog for information on the latest threat trends.
Cyber News Rundown: Anatova Ransomware Infects the Globe
Anatova Ransomware Reaches Global Market
A new ransomware family, dubbed Anatova by researchers, has been infecting machines across the globe. During encryption, Anatova appears to focus on small files to speed up overall encryption times, but doesn’t append the encrypted files with a new extension. Unexpectedly, this variant demands DASH crypto coins, rather than using a currency with a less visible transaction ledger. It also uses several tactics to prevent analysis in both real-world and virtual environments.
Android Malware Remains Dormant until it Detects Motion
On the Google Play store, researchers have discovered several malicious apps that rely on an unusual trigger to install a banking Trojan: motion sensors. By monitoring the motion sensor in a specific mobile device, the malware can determine if it is a real victim device or a research emulator (which would likely remain stationary during analysis.) In particular, one of these insidious apps was downloading the Anubis banking Trojan, which launched a fake Android update screen to start keylogging in hopes of capturing banking credentials.
Google Faces First Major GDPR Fine
Regulators in France have issued a fine against Google for two separate complaints, the first being the company’s misuse of their users’ data, the second being the legal use of that data without providing the user enough details to give fully-informed consent. This fine is the first issued by the CNIL, the official regulator for France, and could cost Google up to $57 million.
ElasticSearch Database Exposes Online Gambling Bets
In the last couple days, security researchers have discovered a database holding sensitive information on dozens of online casino sites’ bettors. After contacting the hosting provider, researchers verified that the database, which contained over 100 million bet entries, had finally been secured. However, it’s still unclear whether the database’s owner or the ISP was responsible.
Chinese Crypto Farms Get Unique Ransomware Strain
Since China houses most of the world’s cryptocurrency mining farms, it comes as little surprise that malware authors are beginning to focus on this lucrative market. By infecting Antminer devices, which mine Litecoin and Bitcoin, this variant can quickly shut down the device and prevent further mining operations. Victims must choose between paying an extremely high ransom and allowing the infection to spread to thousands of other devices. For victims who do not pay, this variant also threatens to shut down devices’ fans, causing them to overheat and eventually destroy themselves.
Smart Wearables: Convenience vs. Security
Fitness trackers and other digital wearables have unlocked a new era of convenience and engagement in consumer health. Beyond general fitness trackers, you can find wearables for a variety of purposes; some help diabetics, some monitor for seizure activity, and some can aid in senior citizens’ health and quality of life. But the convenience of an interconnected lifestyle may be a double-edged sword. Fitness trackers and wearables are notoriously unsecured. Wearables record and store some of our most sensitive health data—which is often 10x more valuable than a stolen credit card— making them a particularly attractive target for hackers.
So what types of data does your fitness tracker store? For a start, it holds the identifying information required to set up your account, such as your email, username, and password. But other fitness tracking specifics can make a user easier to identify, including as gender, birthdate, geographical location, height, and weight. Health and activity data provides an in-depth look at the user’s daily habits through the power of GPS monitoring. If your device is paired inside of a network, other personal device information will also be stored, such as your Unique Device IDs or MAC addresses. Depending on the device, your wearables may also store your credit card information or bank account information.
New vulnerabilities
Because of their versatility, wearables and fitness trackers leave us vulnerable in many ways. In last year’s MyFitnessPal hack, which affected 150 million users, attackers hoped to access credit card information but came away with only usernames and passwords. But what about the information that is more specific to wearables, like GPS tracking? After the fitness tracker Strava revealed hidden army bases through heatmap tracking, the Pentagon began to restrict the use of wearables by military personnel due to the potential security threat. And the recently uncovered MiSafe vulnerability left thousands of children unsecured, allowing hackers to track their movements, listen in on conversations, and actually call children on their smart watches.
Even with these concerns, the wearables market continues to grow, with the prevalence of such devices predicted to double by 2021. Large healthcare organizations and insurance carriers are also starting to use insights from fitness trackers to influence both patient care and insurance rates. We’re even beginning to see the introduction of wearables for employee tracking, although this has met with mixed response. With this increased exposure to potentially insecure technologies, you’ll need to take extra steps to ensure your family’s security.
Where to start
Always research any fitness trackers or wearable devices before you commit, and be sure to avoid devices with any known security flaws. Notable examples to avoid are Medion’s Life S2000 Activity Tracker and Moov’s Now tracker. The Life S2000 requires no authentication and sends data unencrypted, and the Now tracker can leave users vulnerable to attack via Bluetooth connectivity. Even larger brands like Lenovo struggle to maintain an adequate level of security in their fitness trackers; the Lenovo HW01 smart band sends both registration and login data to its servers unencrypted.
Although it’s tedious, we recommend you always read the privacy policy of any wearable device or fitness tracking app before you use it. If the data storage and security measures outlined in the policy aren’t up to snuff, request a refund and let the manufacturer know why. Periodically reviewing your app’s privacy settings on your phone is also a good practice—just to make sure you’re comfortable with the app’s level of access. Take common-sense cybersecurity measures to help keep your wearables as secure as possible. Never reuse passwords or use third party login services like Facebook Login, and consider using a password manager like LastPass® instead.
Wearables and fitness trackers are here to stay, and the Internet of Things (IOT) is only going to keep growing. We have to work together to protect ourselves as we integrate these technologies into our daily lives. After all, the price of convenience cannot match the value of our personal security.
As always, be sure to check back here to stay updated on the newest cybersecurity trends.
Cyber News Rundown: Ransomware Halts Texas Town
Texas Town Brought to a Halt by Ransomware
Several days ago the town of Del Rio, Texas, fell victim to a ransomware attack that knocked most of the town’s major systems offline. While the town’s IT department quickly worked to isolate the infection, remaining departments were forced to switch to hand-written transactions in order to not completely shut down. Fortunately, the attack was quickly resolved and all city websites returned to normal within only a couple of days.
Data Vulnerability Affects Booking Systems for 141 Airlines
Researchers recently discovered a data vulnerability affecting the Amadeus ticket booking system, which is used by more than a hundred international airlines. By making simple changes to a provided URL link, researchers were able to access passenger records and view related flight information. They were also able to access an Israeli airline’s user portal and make changes to the user account, and even change or cancel flight reservations.
Ryuk Ransomware Surpasses $4 Million in Ransom Payments
The ransomware variant known as Ryuk has pulled in nearly $4 million in Bitcoin payments alone since last August. By remaining dormant on previously infected systems, Ryuk can stay hidden for months or even years while its operators build an understanding of the system. In doing so, the attackers are able to command much higher ransom payments by focusing on victims with the means to pay a larger sum.
Account Vulnerability Plaguing Fortnite Players
A new vulnerability has been found pertaining to user accounts for Fortnite that could allow attackers to take full control of an account. By intercepting game-specific authentication tokens, attackers could access a user’s payment card details and use them to purchase in-game currency, or even gain access to a victim’s in-game conversations. Fortunately, Epic Games reacted swiftly to the announced exploits and quickly resolved the security flaws.
Advertising Hack Pushes Malware on Online Shoppers
The latest MageCart attack has compromised the entire distribution network for Adverline, a French advertising company that conducts a substantial amount of business in Europe. By injecting a malicious JavaScript code into dozens of online stores, the attack has been used to steal payment data from at least 277 unique websites thus far. By starting the attack at the top of the distribution chain, these types of attacks have an increased chance of success as the number of victims rises.
MSPs: Your Security Vendor Should Integrate with More Than Just Your RMM and PSA
For many MSPs, integrating their security solution with their remote monitoring and management (RMM) and professional service automation (PSA) platforms is essential for doing business. Together, these platforms help lower the cost of keeping up with each client, ensuring profitable margins for a healthy, growing business.
For true providers of IT services—MSPs that sell services rather than licenses and take a holistic approach to client IT health—RMM and PSA integrations are critical for keeping track of hundreds or even thousands of unique endpoints and automating recurring operations for numerous clients.
Like many of the other features of our security solutions, our RMM and PSA integrations are custom-built with the needs of MSPs in mind. They’re designed to help MSPs create the most efficient, well-oiled versions of their businesses possible so that service is prompt, solutions are effective, and profit is preserved.
Here’s what you should expect from your RMM and PSA security integrations:
- Faster rollouts- One of the core benefits of RMM-assisted deployments, expect rollouts to new endpoints to be fast and hassle-free with well-designed integrations. New endpoints should be easy to set up with protection turned on in just a few clicks.
- Simplified management- Efficiency is key to profitability. So a centralized dashboard displaying what’s running, what’s broken and how, infection statuses, endpoints requiring attention, and more helps increase the number of endpoints a single technician can manage, boosting efficiency and, ultimately, profitability.
- The data you need- The best RMM and PSA integrations make it possible to get the data you need to run a successful business. Whether it’s per-client data for calculating a client’s cost to you, information on policy settings for sites and endpoints, or additional reporting delivered to clients to promote peace-of-mind, having access to allof your data empowers decision-making.
Integrations don’t have to end there
Integrating disparate products can be a laborious, time-intensive process. For that reason, many security vendors are reluctant to coordinate too closely with customers to automate functions unique to their businesses. But it doesn’t have to be that way.
Advanced plugins and tools allow for complete customization of dashboards, reporting, and data tracking. Each can be customized to track the metrics most useful to the organization. Critical processes, like issuing periodic reports, can be fully automated. This can be extremely beneficial when it comes to communicating with customers. Weekly or monthly reports demonstrate that, despite a lack of any major security incidents, it wasn’t for lack of trying on the part of cybercriminals.
More than simply allowing different business platforms to talk to one another, integration plugins can be used for running commands and performing actions. This includes creating, modifying, or deleting licenses, removing duplicate endpoints, or quickly creating new console sites.
Insist on better integrations
So when considering which cybersecurity vendor offers the most for your MSP, consider not only whether the solution allows you to communicate with your RMM and PSA platforms, but also how deeply. Does the vendor have a dedicated integrations team? Do they offer tools for the customization of business-specific reporting? Can essential, recurring business processes be automated?
The answers to the questions above will help you determine how much value RMM and PSA integrations add for your business. In a market where margins can be razor thin and built-in efficiencies can make or break the bottom line, the answers may make all the difference.
Cyber News Rundown: Bad Apps Infect Google Play
Malicious Apps Get Millions of Installs
Google recently removed 85 apps from the Play Store after they were found to contain predatory adware. With over nine million combined downloads, the apps were mostly fake games or utility apps that began pushing a constant stream of full-screen ads to users until the app itself crashed. More worrisome, while nearly all the apps shared similar code, they were mostly uploaded from different developer accounts and used different digital certificates to minimize detection.
Tuition Scam Targets UK College
Several parents of students attending St. Lawrence College in the UK fell victim to an email scam over the holidays that requested early tuition payment at a discounted rate for the upcoming terms. While security measures surrounding parental information have since been improved, at least two separate families confirmed they sent undisclosed amounts of money to the scammers. Though these types of attacks target large audiences, it takes only a small number of successful attempts to make the campaign profitable.
Australian EWN System Hacked
With the help of a strong detection system, a brief hack of the Australian Early Warning Network (EWN) was quickly shutdown. Some of the messages contained warnings about the security of the EWN and listed several links that the user could navigate through. Fortunately, staff were quick to notice the severity of what was occurring and acted to prevent additional customers from being spammed.
Ransomware Uses Children’s Charity as Cover
When CryptoMix first came to light, it included a ransom note masquerading as a request for a “donation” to a children’s charity. It has since returned, but now includes actual information from crowdfunding sites attempting to help sick children and using their stories to guilt victims into paying a ransom. Even worse, as victims navigate the payment process, the ransomware continues to urge them on with promises that the sick child will know their name for the aid they provide.
Exploit Broker Raises Bounties for New Year
Following the New Year, a known exploit broker, Zerodium, announced they would be effectively doubling all bounty payouts for zero-day exploits. While lower-end Windows exploits will net a researcher $80,000, some Android and iOS zero-days will pay out up to $2 million. Unfortunately for many working on the lawful side, nearly all the exploits obtained by Zerodium will be privately sold, rather than used for patching or improving security.
The Must-Have Tech Accessory for Students
We live in a digital age where internet-connected devices are the norm. Our phones, our televisions, even our light bulbs are tied together in today’s tech ecosystem. For high school and college students, this degree of digital connection is the standard, and when school is in session, tech accessories are a popular way to customize the various connected devices that are now an essential part of students’ lives.
With their focus on specialized accessories, it’s easy for students to overlook the importance of securing their connected devices. What’s the point of an expensive phone case or the perfect PopSocket if you’re leaving yourself, and your data, vulnerable? Hacks, security breaches, and stolen identities are often seen as things that don’t happen to digital natives. But security breaches can happen to anyone—no matter how sophisticated a user may be—and are almost always preventable by practicing safe cyber habits and having the right security is in place. But where do you start?
Back to basics
For students at any level, these best practices may seem eye-rollingly intuitive, but they are the basic tools for staying safe and secure online. Flaws with basic cybersecurity often prove to be the catalyst for a chain reaction of breaches, so by making sure these essential fail-safes are in place, you go a long way toward protecting yourself from cybercrime.
Awareness
Being aware of your surroundings and the connectivity of your devices is the first step towards a digitally secure life. But what does awareness mean from a cybersecurity standpoint? It means turning airdrop, file sharing, and open Bluetooth connectivity off, before you use your device in a public area. It means not leaving your laptop unattended, even if you’re just running to the bathroom at the coffee shop. It means using a free tool, such as haveibeenpwned.com, to see if your data has been breached in the past and taking corrective measures if it has been. Most importantly, it means treating public networks like they are public, and not accessing sensitive information through them unless you take the proper precautions (more on that below).
Two-Factor authentication
Two-factor authentication, where a validation message is sent upon login, is a security feature that verifies that you are the one who is actually attempting to access your account, particularly if the access request is coming from an unrecognized device or location. Two-factor authentication is the best way to stop unauthorized users from logging into your accounts. Most social media services offer two-factor authentication, but if you don’t trust them to be up to the task, use a third party service such as Authy or Google Authenticator. SMS and email two-factor authentication measures are demonstrably weaker than other available two-factor measures, and should be avoided if possible (although it’s better than using only a password alone).
Multiple passwords
No one likes to remember multiple passwords, let alone multiple secure passwords. But never reusing passwords is the best way to prevent third-party breaches from affecting multiple accounts. A good tip for varied passwords you can remember? Choose a phrase (or favorite song lyric) and break it down into sections. For example, the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog, becomes three separate passphrases.
- the quick brown
- fox jumps over
- the lazy dog
This is a handy trick to wean yourself off the same two passwords you’ve been using since middle school, and is better than password redundancy. Make sure you include spaces in your passphrases. In the rare case spaces are not allowed, then a phrase without spaces will suffice.
Digging deeper
If the tips above are the metaphorical security sign in the window of your digital life, the measures outlined below are the actual security system. A small amount of additional effort on your part will help keep you safe during your educational career.
Antivirus software
Making sure you have trusted antivirus software running on all devices is one of the most effective ways to stay safe from online threats. A cross-device service, such as Webroot SecureAnywhere® solutions, will keep you safe from potentially malicious emails, files, or apps. An important step to never skip? Keeping your antivirus software up to date. This will help prevent newly surfaced viruses and malware from penetrating your systems. Or, chose cloud-based antivirus solutions, like Webroot’s, that do not require updates.
Password managers
Don’t want to bother with remembering passwords at all? Password managers with secure encryption make generating and storing passwords safe and easy. Many password managers are compatible with common browsers such as Chrome and Firefox, making it easy to securely auto-fill passwords and other forms online.
Message encryption
Encryption services use ciphers to convert messages into random symbols, which are only able to be converted back when accessed by the intended recipient, with a special key. Common encryption options are Apple Messages and Signal, as well as WhatsApp, which is owned by Facebook. If you prefer an encryption option that isn’t owned by a large corporation, Signal is a part of Open Whisper Systems.
Virtual private networks
If you must access sensitive information through a public network, setting up a virtual private network (VPN) will block and redirect your IP address, preventing outside parties from tracking and storing your information. Your VPN setup will largely depend on both your specific devices and price point, but with a little research and energy you can prevent anyone and anything from accessing your digital vault.
Vigilance is key
These tools are the true must-have tech accessories to support young people today and their digitally enhanced life. It’s easy to be overwhelmed as a student with school, work, and social life, but don’t let your cybersecurity defenses lag. Stay informed and stay updated.
Top 5 Things SMBs Should Consider When Evaluating a Cybersecurity Strategy
SMBs are overconfident about their cybersecurity posture.
A survey of SMBs conducted by 451 Research found that in the preceding 24 months, 71% of respondents experienced a breach or attack that resulted in operational disruption, reputational damage, significant financial losses or regulatory penalties. At the same time, 49% of the SMBs surveyed said that cybersecurity is a low priority for their business, and 90% believe they have the appropriate security technologies in place. Clearly, SMBs are not correctly evaluating cybersecurity risk.
Many of us can relate – each day we ignore obvious signs that point to a reality that is in direct contrast to our beliefs. For example, as each year passes, most of us get a little slower, muscles ache that never ached before, we get a bit softer around the middle, and we hold our reading material farther away. Yet, we are convinced we could take on an NBA player in a game of one-on-one or complete the American Ninja Warrior obstacle course on the first try.
While it’s unlikely that most of us can make the improvements needed to compete with elite athletes, the same can’t be said for enterprise cybersecurity. The journey is not an easy one given the security talent vacuum, a lack of domain understanding at the executive level, and the complexity of implementing a long-term, metric-based strategy. But, if you are an SMB struggling to run up and down the proverbial court, here are five things you should consider when building a better security practice:
1. Experienced staff are valuable, but expensive, assets.
Although enterprise cybersecurity is a 24/7/365 effort requiring a full roster of experienced professionals, many SMB cybersecurity teams are underequipped to handle the constant deluge of alert notifications, let alone the investigation or remediation processes. In fact, only 23% of survey respondents plan to add staff to their security teams in the coming year. For many SMBs, the security staffing struggles may get worse as 87% reported difficulties in retaining existing security professionals. To fill this gap, SMBs are increasingly turning to MSPs and MSSPs to provide the expertise and resources needed to protect their organizations around the clock.
2. Executives understand what is at stake, but not what action to take.
As the threat landscape becomes more treacherous, regulatory requirements multiply, and security incidents become more common, executives at SMBs have become more acutely aware of the business impact of security incidents – most are feeling an urgency to strengthen organizational cybersecurity. However, acknowledging the problem is only the first step of the process. Executives need to interface with their internal security teams, industry experts and MSPs in order to fully understand their organization’s risk portfolio and design a long-term cybersecurity strategy that integrates with business objectives.
3. Security awareness training (SAT) is low-hanging fruit (if done right).
According to the 451 Research Voice of the Enterprise: Information Security: Workloads and Key Projects survey, 62% of SMBs said they have a SAT program in place, but 50% are delivering SAT on their own using ‘homegrown’ methods and materials. It should be no surprise that many SMBs described their SAT efforts as ineffective. MSPs are increasingly offering high-quality, comprehensive SAT for a variety of compliance and regulatory frameworks such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, SOX, ISO, GDPR and GLBA. SMBs looking to strengthen their security posture should look to partner with these MSPs for security awareness training.
4. Securing now means securing for the future.
The future of IT architecture will span both private and public clouds. This hybrid- and multi-cloud infrastructure represents a significant challenge for SMBs that require a cybersecurity posture that is both layered and scalable. SMBs need to understand and consider long-term trends when evaluating their current cybersecurity strategy. With this aim in mind, SMBs can turn to MSPs and MSSPs with the experience and toolsets necessary for securing these types of complex environments.
5. A metrics-based security approach is needed for true accountability.
In a rush to shore up organizational security, SMBs might make the all-too-common mistake of equating money spent with security gained. To be clear: spending not backed by strategy and measurement only enhances security posture on the margins, if at all. To get the most bang for each buck, SMBs need to build an accountable security system predicated on quantifiable metrics.Again, this is an area where SMBs can partner with MSPs and MSSPs. This serves as an opportunity to develop cybersecurity strategy with measurable KPIs to ensure security gains are maintained over time. MSPs can help SMBs define the most applicable variables for their IT architectures, whether it be incident response rate, time-to-response or other relevant metrics.
The strategic reevaluation of organizational security is a daunting task for any organization, but given the risks SMBs face and their tendency to be underprepared, it is a necessary challenge. These key points of consideration for SMBs embarking on this critical journey underscore the importance of building an accountable and forward-looking security system and highlight the ways in which SMBs can work alongside MSP or MSSP partners to implement the right cybersecurity system for their organizations. I hope this will be the wake-up call all SMBs need to unleash their inner cybersecurity all-star.
If you’re interested in learning more about how other SMBs are approaching cybersecurity, read my report Security Services Fueling Growth for MSPs.
Cyber News Rundown: Ransomware Hits Tribune Publishing
American Newspapers Shutdown After Ransomware Attack
Nearly all news publications owned by Tribune Publishing suffered disruptions in printing or distribution after the publisher was hit by a ransomware attack. Many of the papers across the country were delivered incomplete or hours or days late. Even some papers that had been sold off to other publishers in previous years were affected. Fortunately, digital and mobile versions of the newspapers were untouched by the attack, allowing users to view local news as normal online.
‘PewDiePie’ Hacker Turns Focus to Smart Devices
The hacker previously responsible for hacking thousands of printers and directing them to print ads in support of PewDiePie, the world’s largest YouTuber, has now started using unsecured smart devices to continue the campaign. In addition to requesting the “victim” subscribe to PewDiePie, the hacker’s main message is to bring light to the extreme lack of security many of us live with daily. By using the standard ports used by smart TVs to connect to streaming devices, the hacker has even created scripts that will search for these insecure ports and begin connecting to them.
California Alcohol Retailer Faces Data Breach
One of the largest alcohol retailers in California, BevMo, recently announced they’ve fallen victim to a credit card breach on their online store. The breach lasted for nearly two months, during which time customer payment card data for nearly 14,000 customers was illegitimately accessed. While officials are still unclear as to who was behind the breach, it is likely related to the MageCart attacks that appeared across the globe during the latter half of 2018.
Blur Password Manager Leaves Passwords Exposed
An independent security researcher recently discovered a server that was allowing unauthenticated access to sensitive documents for well over two million users. The exposed information included names, email addresses, IP addresses from prior logins, and even their account password, though the company has remained firm that the passwords contained within their accounts are still secure. Since the reveal, Blur’s parent company, Abine, has prompted users to change their main passwords and enable two-factor authentication, if they had not already done so.
Bitcoin Wallets: Still Major Target for Hackers
Nearly $750,000 worth of Bitcoin was stolen from Electrum wallets in an attack that began only a few days before Christmas. By exploiting a previously documented vulnerability, the hackers were able to inject their own server list into the connections made by the Electrum wallet and successfully rerout their victims to another server, where they were then presented with a fake update screen. By moving forward with the “update,” malware was promptly downloaded to the device and users could then enter their wallet credentials, only for them to be stolen and their accounts drained.
Cyber News Rundown: Amazon User Receives Thousands of Alexa-Recorded Messages
Amazon User Receives Thousands of Alexa-Recorded Messages
Upon requesting all his user data from Amazon, one user promptly received over 1,700 recorded messages from an Alexa device. Unfortunately, the individual didn’t own such a device. The messages were from a device belonging to complete stranger, and some of them could have easily been used to find the identity of the recorded person. While Amazon did offer the victim a free Prime membership, it’s cold comfort, as these devices are constantly recording and uploading everyday details about millions of users.
San Diego School District Hacked
In a recent phishing scheme, hackers successfully gained the trust of a San Diego Unified School Districtemployee and obtained credentials to a system that contained student, parent, and staff data from the past decade. The database mostly consisted of personal data for over half a million individuals, but also included student course schedules and even payroll information for the District’s staff.
Data Breach Affects Hundreds of Coffee Shops
Attackers were able to access payment data for 265 Caribou Coffee shopsacross the United States. The breach could affect any customers who made purchases between the end of August 2018 and the first week of December. The company recommends that any customers who may have visited any of their locations across 11 states engage a credit monitoring service to help avoid possible fraud.
FBI Shuts Down DDoS-for-Hire Sites
At least 15 DDoS-for-Hire siteshave been taken down in a recent sweep by the U.S. Justice Department, and three site operators are currently awaiting charges. Some of the sites had been operating for more than 4 years and were responsible for over 200,000 DDoS attacks across the globe. This is the second in a series of government-led cyberattack shutdowns over the last year.
Email Scam Offers Brand New BMW for Personal Info
A new email scam is informing victims that they’ve just won a 2018 BMW M240iand over $1 million dollars, which they can easily claim if they provide their name and contact information. Victims who provide their contact details are then contacted directly and asked to give additional information, such as their social security number and credit or bank card details. If you receive this email or one like it, we recommend you delete it immediately, without opening it.
Cybersecurity Trends to Watch Out for in 2019
The cybersecurity landscape is in constant flux, keeping our team busy researching the newest threats to keep our customers safe. As the new year approaches, we asked our cybersecurity experts to predict which security trends will have the most impact in 2019 and what consumers should prepare for.
Continued Growth of Cryptojacking
“Cryptojacking will continue to dominate the landscape. Arguably more than a third of all attacks in 2019 will be based off of leveraging hardware in your devices to mine cryptocurrency.” – Tyler Moffitt, Senior Threat Research Analyst
The largest cyber threat of 2018 will continue its unprecedented growth in 2019. Cryptojacking—a type of hack that targets almost any device with computing power, including mobile devices, company servers, and even cable routers to mine for cryptocurrencies—grew by more than 1,000% in the first half of 2018. Compared to ransomware attacks, cryptojacking is incredibly stealthy, with many systems losing processing power while sitting idle anyway. We are now seeing cryptojacking in more significant systems, as was the case when Nova Scotia’s St. Francis Xavier University struggled for weeks to recover after cryptojacking software led to the school to disable its entire digital infrastructure in order to purge the network. For home internet users, cryptojacking can put undue stress on your computer’s processor, slowing down performance and increasing your electric bill.
But, as with any cybersecurity threat, it’s a constant cat-and-mouse game between criminals and the security industry. As cryptojacking continues to grow, so does criminals’ ability to successfully implement the attack. At the same time, so does our knowledge and ability to defend against it. This type of attack can impact your devices in multiple ways, whether via a file on your computer or a website you visit. We recommend a layered solution that can protect against these different attack vectors, like Webroot SecureAnywhere® solutions.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) Influence
“We are going to see a lot more legislation proposed within the US that will be very similar to GDPR, much like California already has. These types of laws will inspire the idea that companies don’t own data that identifies people, and we need to be better stewards of that data. Data, by all accounts, is a commodity. It’s necessary for innovation and to stay competitive, but the data must be good to be of any use.” – Briana Butler, Engineering Data Analyst
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a set of regulations put in place in 2018 that standardize data protection measures within the European Union, marking the beginning of a new era of international data protection. In the United States, California has been on the frontlines of data protection law since 2003 when bill SB1386 was passed, pioneering mandatory data-breach notifications nationwide. California continues to innovate in data privacy law with the recently passed California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA), possibly the toughest data privacy law in the country. Although clearly influenced by GDPR, it differs in many ways—enough that companies who are compliant with GDPR may need to take additional steps to also be compliant under the CCPA. But it’s not just lawmakers who are pushing for data protection regulation, influential tech industry leaders like Tim Cook are also calling for stronger consumer protections on data collection nationwide.
What does this mean for you? Expect another wave of “Privacy Update” emails and cookie collection pop-up notices while browsing, as well as expanded protections regarding the collection and storage of your personal data. Given the rising regularity of third party data breaches—like the one that recently left 500 million Marriott guests exposed—stronger data protection laws can only mean good things for consumers.
Biometrics on the Rise
“We will see continued growth in biometric services. Devices with usernames and passwords will become the legacy choice for authentication.” – Paul Barnes, Sr. Director of Product Strategy
Largely associated with facial and fingerprint recognition, biometrics have been on the rise since at least 2013, when the launch of TouchID placed the technology in every iPhone user’s hands. But the adoption of biometric technologies—particularly facial recognition biometrics—was dampened by cultural and ethical concerns, with some fearing the establishment of a national biometric database. But today we are beginning to see the normalization of facial recognition biometrics, like those utilized by Snapchat and Instagram. Biometrics are also now widely seen used in critical infrastructure applications. Airports use biometrics to facilitate a faster boarding process, and hospitals are adopting biometrics for both patient care and as a HIPAA security precaution.
We predict this regular exposure to biometrics will lead to a larger cultural acceptance and adoption of biometrics as a trusted security standard, leading to the eventual death of usernames and passwords. Why bother with a login when your computer knows the minute details of your iris? But convenience may come as a cost. Corresponding with rising use, biometric data will continue to become a more valuable commodity for cybercriminals to steal.
The Beginning of the End for SSNs
“There will be significant discussion around replacing Social Security numbers for a more secure, universal personal identity option.” – Kristin Miller, Director of Communications
In 2017 the Equifax breach compromised 145.5 million Social Security numbers, forcing us to face an uncomfortable truth: SSNs are a legacy system. First available in 1935 from the newly minted Social Security Administration, they were created to track accounts using Social Security programs. They were never intended to act as the secure database key we expect them to be today.
The conversation has already begun on the federal level. “I think it’s really clear there needs to be a change,” White House Cybersecurity Coordinator Rob Joyce said at the 2017 Cambridge Cyber Summit. “It’s a flawed system. If you think about it, every time we use the Social Security number you put it at risk.”
Although it will be some time until we fully replace Social Security numbers, what should you expect from a replacement? When it comes to personal identifiers that are both unique and secure, the conversations tend to center around two technologies: biometrics and blockchains. Biometrics—particularly behavioral biometrics, which derive their logic from individual’s behavioral patterns, such as the syncopation of types or taps on a screen, or even your unique heart beat—are proving to be an especially intuitive solution.
Certification for the Internet of Things
“We will finally see a consumer IoT/connected goods certification body, similar to the Consumer Electrical Safety Certifications today. This will enforce the notion of Security by Design for a smart goods manufacturer.” – Paul Barnes, Sr. Director of Product Strategy
We love the Internet of Things (IoT). It powers our smart homes, our fitness trackers, and our voice assistants. But IoT devices are notoriously insecure, oftentimes featuring overlooked flaws that can lead to exploitation in unexpected places. A recent Pew Research Center survey looked at how growing security concerns are influencing the spread of IoT connectivity reported only 15% of participants saying security concerns would cause significant numbers of people to disconnect from IoT devices. Alternatively, 85% believe most people will move more deeply into an interconnected life due to the convenience of IoT products. Recently published documents may signal that the time of putting convenience ahead of security is quickly coming to an end.
The United Kingdom’s department for Digital, Culture, Media, and Sport (DCMS) published the “Code of Practice for Consumer IoT Security.” The code outlines thirteen steps for organizations to follow for the implementation of appropriate security measures in IoT offerings. It also emphasizes the need for a secure-by-design philosophy, a belief that security measures need to be designed into products, not bolted on afterwards. This type of regulatory influence on the industry is sure to make waves across the pond, and we are already seeing this play out with California’s new IoT security law.
Keep these predictions in mind as you make your way through 2019. Staying informed is the best way to keep you and your family safe, so check back here for more cybersecurity trend updates in the future!