
by Blog Staff | Feb 17, 2012 | Threat Lab
We’ve all seen software grow. We watch as our favorite software adds on new features and becomes better at what it does. Malware writers are no different, they want their software to have more features as well as steal even more information. PJApps is a good example of this. PJApps is a Trojan that’s been around for a while causing havoc by being bundled in legitimate applications found in alternative Android markets, it is capable of opening a backdoor, stealing data and blocking sms behind the scenes. In one variant of PJApps it requests the following permissions to steal information:
INTERNET
RECEIVE_SMS
SEND_SMS
READ_HISTORY_BOOKMARKS
WRITE_HISTORY_BOOKMARKS
INSTALL_PACKAGES
WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE
READ_PHONE_STATE
Here’s some of things the older variants of PJApps stole:
-SIM Card Number
-Telephone Number
-IMSI Number

(more…)

by Blog Staff | Feb 17, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
Which is the most targeted mobile operating system?
According to the recently released 2011 Mobile Threats Report from our partners at Juniper Networks, that’s the Android OS.
Key summary points from the report:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Feb 17, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
Cybercriminals are currently spamvertising a “You just received a e-card form somebody” themed malware campaign, impersonating Hallmark.

More details:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Feb 15, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
On Monday, Twitter announced that it’s introducing support for secure HTTPS connections to all users by default.

More details:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Feb 14, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
According to a newly released report from NSS Labs, Microsoft’s Internet Explorer 9 outperforms competing browsers in protecting against socially engineered malware.
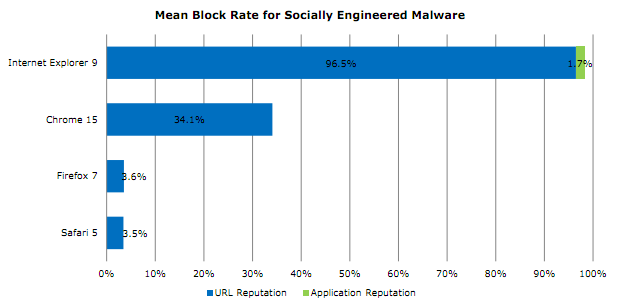
More details:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Feb 10, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
A well known group of hackers has penetrated the networks of the United Nations, according to a note posted on Pastebin.com.

The group claiming responsibility is Team Poison, a hacking group closely associated with the Anonymous hactivist movement. Team Poison members include TriCk, iN^SaNe, MLT,Phantom~, C0RPS3, f0rsaken, aXioM and ap0calypse.
More details:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Feb 10, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
What are pharmaceutical scammers up to? From active participation in black hat search engine optimization campaigns, to spamvertising of bogus links — including QR Codes — and compromising of web sites with high page rank in order to redirect to pharmaceutical scams, scammers are keeping themselves pretty busy in order to monetize as much web traffic as possible.
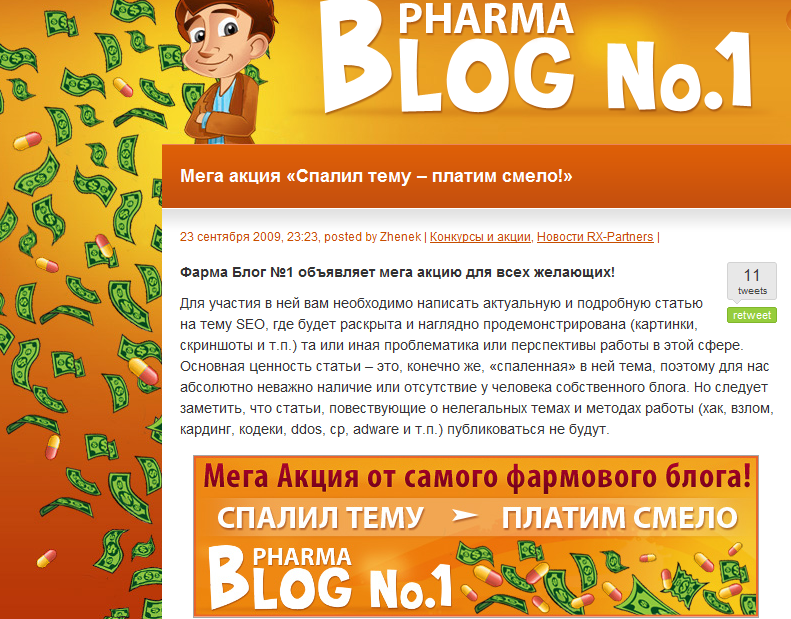
Recently, one of the most popular affiliate network for selling counterfeit pharmaceutical items launched its own Web contest.
Let’s take a look.
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Feb 8, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
Security researchers from Webroot have intercepted two currently live client-side exploits serving malware campaigns that have already managed to infect over 20,000 PCs across the globe, primarily in the United States. Based upon detailed analysis, it can be concluded that both campaigns are launched by the same cybercriminal.
More details:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Feb 8, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
Security researchers from “Tracking Cyber Crime” have spotted a new ZeuS crimeware variant, that’s based on the leaked ZeuS source code from last year.
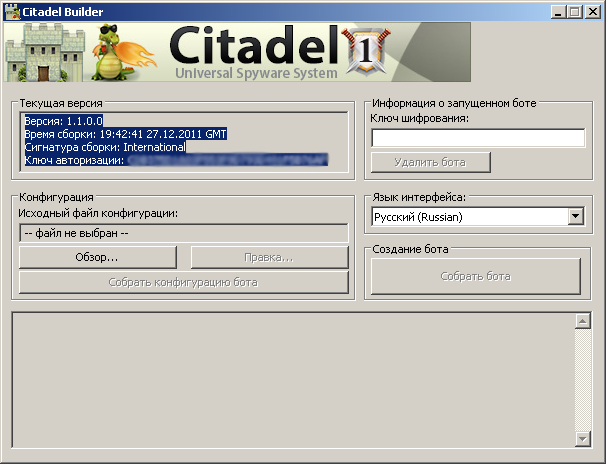
Dubbed Citadel, the crimeware is positioned as a universal spyware system, whose modular nature allows cybercriminals to offer flexibly priced value-added services such as managed malware crypting, and managed web injects as a service.
Some of Citadel’s core features include:
(more…)

by Blog Staff | Feb 3, 2012 | Industry Intel, Threat Lab
The competitive arms race between security vendors and malicious cybercriminals constantly produces new defensive mechanisms, next to new attack platforms and malicious tools aiming to efficiently exploit and infect as many people as possible.
Continuing the “A peek inside…” series, in this post I will profile yet another malware loader. This time it’s the Smoke Malware Loader.
(more…)
















